点击下载 LICEcap
Unity学习路径
如何让Unity Mixer混合器音量控制符合体感
Unity Mixer是什么
游戏中的声音轨道有很多,使用Unity提供Mixer混响可以很方便按组控制音量,只需要暴露变量给代码,就可以调用Mixer.SetFloat("变量", 数值),数值单位是db。
Unity Mixer修改音量为什么不符合体感
真实世界中的声音通过震动产生,
人耳感受最小声压 :
2×10^{-5} (db)
人耳感受最大声压:
2×10^{-1} (db)
Mixer采用的单位是db,最高0db,最低-80db,以模拟真实世界。但是按照直觉我们拖动进度条控制音量[0,-80]反而觉得音量变化不是线性的。这需要看声压级公式:
LP(db) = 10Log_{10}^{(\frac{p}{p0})}
推导求声压比公式:
(\frac{p}{p0}) = 10^\frac{Lp}{10}
当声压级按[0,-80]线性变化时,体感音量(声压比 p/p0)的变化是对数变化,因此如果需要体感音量按线性变化,那么就对LP进行转换。
convertToLp(volume:number){
let lp = 10 * Math.Log10(volume)
lp = Math.max(-80, lp)
return lp
}
convertToVolump(db:number){
let volume = Math.pow(10, db/10)
//体感最小音量
if(volume <= Math.pow(10, -5))
volume = 0
return volume
}Unity Timeline 手动更新
this.director.timeUpdateMode = UnityEngine.Playables.DirectorUpdateMode.Manual
PlayeBetween(start:number, seconds: number){
this.isPaused = false
this.director.time = start
this.targetTime = seconds
this.director.Resume()
}
private UpdateTime(t:number){
if(this.isPaused)return
let director = this.director
let targetTime = this.targetTime
let deviation = this.devation
if (director.time > targetTime + deviation)
{
director.time -= t;
director.Evaluate();
}
else if (director.time < targetTime - deviation)
{
director.time += t;
director.Evaluate();
}
else if (director.time != targetTime)
{
director.time = targetTime;
director.Evaluate();
}
}常用linux指令
原文: 《Linux就该这么学》
man [指令]
帮助文档
| 按键 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| 空格键 | 向下翻页 |
| Page down | 向下翻页 |
| Page up | 向上翻页 |
| home | 直接前往首页 |
| end | 直接前往尾页 |
| / | 从上向下搜索如:/linux |
| ? | 从下向上搜索如:?linux |
| n | 定位到下一个搜索到的关键词 |
| N | 定位到上一个搜索到的关键词 |
| q | 退出帮助文档 |
Ctrl + d
表示键盘输入结束
Ctrl + l (小写L)
清屏
echo [字符串] [$变量]
输出到终端,常用于输出字符串、变量
[root@VM-4-13-centos ~]# echo "hello world"
hello world
[root@VM-4-13-centos ~]# echo $SHELL
/bin/bash
date [+指定格式]
常用于设置、显示系统的时间与日期
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| %S | 秒(00~59) |
| %M | 分钟(00~59) |
| %H | 小时(00~23) |
| %I | 小时(00~12) |
| %m | 月份(1~12) |
| %p | 显示AM或PM |
| %a | 缩写的工作日名称如:Sun |
| %A | 完整的工作日名称如:Sunday |
| %b | 缩写的月份名称如:Jan |
| %B | 完整的月份名称如:January |
| %q | 季度(1~4) |
| %y | 简写年份如:20 |
| %Y | 完整年份如:2020 |
| %d | 本月中的第几天 |
| %j | 今年中的第几天 |
| %n | 换行符 回车 |
| %t | 跳格 tab |
按默认格式查看当前系统时间的命令如下
[root@VM-4-13-centos ~]# date
Sat Sep 5 09:13:45 CST 2020按 年-月-日 时:分:秒 的格式查看的命令如下
[root@VM-4-13-centos ~]# date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
2022-06-10 14:02:39timedatectl [参数]
用于设置系统时间,常用于修改时区
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| status | 显示状态信息 |
| list-timezones | 列出已知时区 |
| set-time | 设置系统时间 |
| set-timezone | 设置生效时区 |
[root@VM-4-13-centos ~]# timedatectl status
Local time: Fri 2022-06-10 14:12:31 CST
Universal time: Fri 2022-06-10 06:12:31 UTC
RTC time: Fri 2022-06-10 06:12:30
Time zone: Asia/Shanghai (CST, +0800)
NTP enabled: no
NTP synchronized: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: n/a
reboot
重启系统
poweroff
关机
wget [参数] 网址
用于从网络中下载文件
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -b | 后台下载模式 |
| -P | 下载到指定目录 |
| -t | 最大尝试次数 |
| -c | 断点续传 |
| -p | 下载页面内所有资源包括图片、视频 |
| -r | 递归下载 |
ps [参数]
用于查看系统中的进程状态,英文全称“processes”
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -a | 显示所有进程(包括其他用户的) |
| -u | 用户以及其他详细信息 |
| -x | 显示没有控制终端的进程 |
Linux系统中有着许多进程,它们有5种常见进程状态
| 状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| R(运行) | 进程正在运行或再队列中等待 |
| S(中断) | 进程处于休眠中,当某个条件形成后或接收到信号时则脱离该状态 |
| D(不可中断) | 进程不响应系统异步信号,即使kill命令也不能将其中断 |
| Z(僵死) | 进程已终止,但进程描述符依然存在,直到父进程调用wait4()系统函数后将进程释放 |
| T(停止) | 进程收到停止信号后停止运行 |
除了上面5种常见的进程状态,还有可能的5种补充形式:高优先级(<)、低优先级(N)、被锁进内存(L)、包含子进程(s)、多线程(l)
当执行 ps -aux命令后,通常会有以下输出值
| USER | PID | %CPU | %MEM | VSZ | RSS | TTY | STAT | START | TIME | COMMAND |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 进程的所有者 | 进程ID号 | cpu占用率 | 内存占用率 | 虚拟内存使用量KB | 占用的固定内存量KB | 所在终端 | 进程状态 | 被启动的时间 | 实际使用cpu的时间 | 命令名称与参数 |
| root | 1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 125508 | 3772 | ? | Ss | May15 | 5:28 | /usr/lib/system |
| root | 2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | ? | S | May15 | 0:00 | [kthreadd] |
| root | 4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | ? | S< | May15 | 0:00 | [kworker/0:0H] |
pstree
以树状图形式显示进程之间的关系
top
用于动态的监视进程活动以及系统负载信息,类似window任务管理器
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# top
top - 14:40:15 up 25 days, 23:30, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
Tasks: 87 total, 2 running, 85 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 0.0 us, 0.0 sy, 0.0 ni,100.0 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.0 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 1881840 total, 757460 free, 228152 used, 896228 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 0 total, 0 free, 0 used. 1481148 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
27 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 md
28 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 edac-poller
...第1行:系统时间、运行时间、登录终端数、系统负载(3个数值分别为1分钟、5分钟、15分钟内的平均值,数值越小意味着负载越低)。
第2行:进程总数、运行中的进程数、睡眠中的进程数、停止的进程数、僵死的进程数。
第3行:用户占用资源百分比、系统内核占用资源百分比、改变过优先级的进程资源百分比、空闲的资源百分比等。其中数据均为CPU数据并以百分比格式显示,例如“99.9 id”意味着有99.9%的CPU处理器资源处于空闲。
第4行:物理内存总量、内存空闲量、内存使用量、作为内核缓存的内存量。
第5行:虚拟内存总量、虚拟内存空闲量、虚拟内存使用量、已被提前加载的内存量。
nice [优先级数字] [服务名称]
用于调整进程的优先级
在top命令输出的结果中,PR和NI代表的是进程的优先级,数字越低,优先级越高,例如讲bash的服务优先级调至最高
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# nice -n -20 bashpidof [参数] 服务名称
用于查询某个指定服务进程的PID
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# pidof sshd
18629 1057kill [参数] 进程PID
用于终止指定PID的服务进程
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# kill 18629如果有时系统提示进程无法被终止,此时可以加参数 -9 表示最高级别地强制杀死进程
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# kill -9 18629killall [参数] 服务名称
用于终止某个指定名称地服务所对应的全部进程
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# pidof httpd
13581 13580 13579 13578 13577 13576
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# killall httpd
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# pidof httpd
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]#ifconfig [参数] [网络设备]
用于获取网卡配置与网络状态等信息,英文全称“interface config”
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# ifconfig
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.0.4.13 netmask 255.255.252.0 broadcast 10.0.7.255
inet6 fe80::5054:ff:fe32:2f7a prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 52:54:00:32:2f:7a txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 23500110 bytes 3944482374 (3.6 GiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 52720153 bytes 6761279874 (6.2 GiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 2767000 bytes 170296940 (162.4 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 2767000 bytes 170296940 (162.4 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
uname [-a]
查看当前系统的内核名称、主机名、内核发行版本、节点名、压制时间、硬件名称、硬件平台、处理器类型以及操作系统名称
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# uname -a
Linux VM-4-13-centos 3.10.0-1160.45.1.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed Oct 13 17:20:51 UTC 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux如果要查看当前系统版本的详细信息则需要查看redhat-release文件
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.6.1810 (Core)uptime
用于查看系统负载,平均负载值是最近1分钟、5分钟、15分钟内的压力情况
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# uptime
15:12:21 up 26 days, 2 min, 1 user, load average: 0.02, 0.02, 0.05free [-h]
用于显示当前系统中内存的使用量信息,带上参数-h以更人性化的方式输出当前内存使用量信息
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1.8G 222M 738M 560K 877M 1.4G
Swap: 0B 0B 0Bwho
用于查看当前登入主机的用户端信息
last
用于查看主机被访问记录
ping [参数] 主机地址
用于测试主机之间的网络连通性
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -c | 发送次数 |
| -l | 指定网卡名称 |
| -i | 每次间隔时间秒 |
| -W | 最长等待时间秒 |
tracepath [参数] 域名
测试数据包到达主机时途中经过的所有路由信息
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# tracepath www.loveuhouse.cn
1?: [LOCALHOST] pmtu 1500
1: 9.112.63.130 4.955ms
1: 9.112.63.130 1.873ms
2: 9.112.123.62 6.560ms
3: 10.196.39.249 0.738ms
4: 10.196.95.33 26.646ms asymm 11
5: 103.216.40.40 31.500ms asymm 9
6: 10.200.43.166 23.873ms asymm 9
7: 117.49.44.166 32.730ms asymm 8
8: 103.216.40.40 30.296ms asymm 9
9: 45.112.216.157 34.218ms
10: 45.112.221.186 32.006ms asymm 8
11: 119.38.215.29 27.570ms asymm 9
12: no reply
13: no reply
14: no reply
...netstat [参数]
用于显示网络链接、路由表、接口状态等完了过信息,英文全称为“network status”
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -a | 显示所有链接中的Socket |
| -p | 显示正在使用的Socket |
| -t | 显示TCP协议的链接状态 |
| -u | 显示UDP协议的链接状态 |
| -n | 使用IP地址,不使用域名 |
| -l | 仅列出正在监听的服务状态 |
| -i | 显示网卡列表信息 |
| -r | 显示路由表信息 |
history [-c]
用于显示执行过的命令历史, 参数-c可以清空所有的命令历史记录
还能用“!编码数字”来重复执行某一次的命令
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# history
1 2022-06-10 13:43:48
2 2022-05-15 15:10:02 ls
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# !2
ls历史命令会被保存到用户home目录的.bash_history文件中,Linux系统中以(.)开头的文件均标识隐藏文件
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# cat ~/.bash_history
#1652598602
ls
#1652598628
wget https://img.zeruns.tech/down/jdk-8u261-linux-x64.tar.gz
#1652598653
mkdir /usr/local/java/
...sosreport
用于手机系统配置及架构信息并输出诊断文档,常用于诊断系统问题
pwd
用于显示用户当前所在工作目录,英文全称为“print working directory”
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# pwd
/root/jancd [参数] [目录]
用于切换当前工作路径,英文全称“change directory”
除了常见的切换目录方式,还能用
cd -返回上一次所处的目录
cd ..进入上级目录
cd ~切换到home目录
cd ~ username切换到其他用户的home目录
ls [参数] [文件名]
用于显示目录中的文件信息
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# ls -al
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jun 10 10:46 .
dr-xr-x---. 11 root root 4096 Jun 10 10:46 ..如果要查看目录,需要额外添加一个-d参数
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# ls -ld /etc
drwxr-xr-x. 94 root root 12288 May 20 13:42 /etctree
用于以树状图的方式列出目录内容及结构
find [查找范围] [寻找条件]
用于按照指定条件来查找文件所对应的位置
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -name | 匹配名称 |
| -perm | 匹配权限(mode完全匹配, -mode为包含) |
| -usr | 匹配所有者 |
| -group | 匹配所有组 |
| -mtime -n +n | 匹配修改内容的时间(-n指n天以内 +n指n天以前) |
| -atime -n +n | 匹配访问文件的时间 |
| -ctime -n +n | 匹配修改文件权限的时间 |
| -nouser | 匹配无所有者的文件 |
| -nogroup | 匹配无所有组的文件 |
| -newer f1 !f2 | 匹配比f1新但比f2旧的文件 |
| -type b/d/c/p/l/f | 匹配文件类型(块设备、目录、字符设备、管道、链接文件、文本文件) |
| -size | 匹配文件大小(+50KB指查找超过的文件, -50KB指查找小于的文件) |
| -prune | 忽略某个目录 |
| -exec | 后面可跟用于进一步处理搜索结果的命令 |
根据文件系统层次标准(Filesystem Hierarchy Standard)协议,Linux系统中的配置文件会保存到/etc目录中,如果想要获取该目录中所有host开头的文件列表
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# find /etc -name "host*" -print
/etc/hosts.deny
/etc/hostname
/etc/cloud/templates/hosts.suse.tmpl
/etc/cloud/templates/hosts.debian.tmpl
/etc/cloud/templates/hosts.redhat.tmpl
/etc/cloud/templates/hosts.freebsd.tmpl
/etc/hosts
/etc/selinux/targeted/active/modules/100/hostname
/etc/hosts.allow
/etc/host.conf如果想要在整个系统搜权限中包括SUID权限的所有文件,只需使用-4000即可
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# find / -perm -4000 -print
/usr/lib/polkit-1/polkit-agent-helper-1
/usr/bin/pkexec
/usr/bin/mount
/usr/bin/passwd
/usr/bin/umount
/usr/bin/newgrp如果要在整个文件系统中找到所有归属于janing用户的文件并复制到/root/findresults目录中,将要使用-exec {} \的参数,其中{}代表find命令搜索出的每一个文件,并且命令的结尾必须是\
find / -usr janing -exec cp -a {} /root/findresults/ \locate [文件名称]
用于按照名称快速搜索文件所对应的位置,在使用locate命令时,先使用updatedb命令生成一个索引库文件,这个库文件的名字是/var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db后续在使用locate命令搜索文件时就是在该库中进行查找操作
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# updatedb
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# ls -l /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db
-rw-r----- 1 root slocate 2521187 Jun 10 16:16 /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# locate whereis
/usr/bin/whereis
/usr/share/bash-completion/completions/whereis
/usr/share/man/man1/whereis.1.gzwhereis [命令名称]
用于按照名称快速搜索二进制程序(命令)、源码、以及帮助文件所对应的位置
简单来说whereis也是基于updatedb所生成的索引库进行搜索,它与locate命令的区别时不关心那些相同名称的文件,仅仅是快速找到对应的命令为你教案以及帮助文件
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# whereis node
node: /usr/bin/nodewhich [命令名称]
用于按照指定名称快速搜索二进制程序(命令)所对应的位置,which命令是在PATH变量所指定的路径中查找,既不关心同名文件也不关心命令所对应的源代码和帮助文件
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# which node
/usr/bin/nodecat [参数] 文件名称
用于查看内容较少的纯文本文件,英文全称为“concatenate”,如果想要显示行号,可以增加-n参数
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# cat -n /etc/redhat-release
1 CentOS Linux release 7.6.1810 (Core)more [参数] 文件名称
用于查看内容较多的纯文本文件,使用空格或回车向下翻页
head [参数] 文件名称
用于查看纯文本文件的前几行
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# head -n 5 /usr/share/autoconf/autom4te.cfg
# Definition of Autom4te option sets. -*- Makefile -*-
#
# Copyright (C) 2001-2012 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modifytail [参数] 文件名称
用于查看纯文本文件的后n行或持续刷新文件的最新内容
当你向查看持续刷新的文件内容可以使用-f参数
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# tail -f /var/log/messagetr [原始字符] [目标字符]
用于替换文本内容中的字符,英文全称为“transform”
比如要把文本全部改为大写
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# cat hello.txt
hello world
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# cat hello.txt | tr [a-z] [A-Z]
HELLO WORLDwc [参数] [文件名称]
用于统计指定文本文件的行数、字数或字节数,英文全称“word counts”
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -l | 只显示行数 |
| -w | 只显示单词数 |
| -c | 只显示字节数 |
在Linux系统中/etc/passwd是用于保存所有用户信息的文件,要统计当前系统有多少个用户,可以使用下面的命令来查询
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# wc -l /etc/passwd
26 /etc/passwdstat [文件名称]
用于查看文件的具体储存细节和时间等信息
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# stat hello.txt
File: ‘hello.txt’
Size: 12 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 665210 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Access: 2022-06-10 16:35:14.426104440 +0800
Modify: 2022-06-10 16:35:14.385104450 +0800
Change: 2022-06-10 16:35:14.385104450 +0800
Birth: -| grep [参数] [文件名称] 用于提取文本内容,以下参数最为常用 |
参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| -n | 用来显示搜索到的信息的行号 | |
| -v | 用来反选信息 | |
| -b | 将可执行文件当作文本文件来搜索 | |
| -c | 仅显示找到的行数 | |
| -i | 忽略大小写 |
Linux系统中/etc/passwd保存所有的用户信息,而一旦用户登录终端被设置成/sbin/nologin则不再允许登录系统,因此可以查找当前系统中不允许登录系统的用户
[root@VM-4-13-centos ~]# grep /sbin/nologin /etc/passwd
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
...cut [参数] [文件名称]
用于按列提取文本内容
比如提取passwd文件中的用户名信息-f设置需要查看的列数-d设置分割符
[root@VM-4-13-centos ~]# cut -d : -f 1 /etc/passwd
root
bin
daemondiff [参数] [文件A] [文件B]
比较多个文件之间内容的差异,可以使用--brief参数来确认两个文件是否相同,还可以使用-c来详细比较多个文件的差异之处
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# diff hello.txt hello2.txt
1c1
< hello world
---
> hello world 2uniq [参数] [文件名称]
用于去除文本中连续的重复行
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# uniq hello.txtsort [参数] [文件名称]
对文本内容再排序,还能使用-u参数进行去重,-t指定间隔符,-k指定第几列,-n数字排序
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -f | 忽略大小写 |
| -b | 忽略缩进与空格 |
| -n | 以数值型排序 |
| -r | 反向排序 |
| -u | 去除重复行 |
| -t | 指定间隔符 |
| -k | 设置字段范围 |
touch [参数] [文件名]
用于创建空白文件或设置文件时间,touch abc可以快速创建一个名为abc的空白文本文件
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| -a | 仅修改读取时间 |
| -m | 仅修改修改时间 |
| -d | 同时修改atime与mtime |
mkdir [参数] [目录名称]
用于创建空白目录,可以结合-p来递归创建出具有嵌套层叠关系的目录
[root@VM-4-13-centos jan]# mkdir -p a/b/c/d/ecp [参数] [源文件] [目标文件]
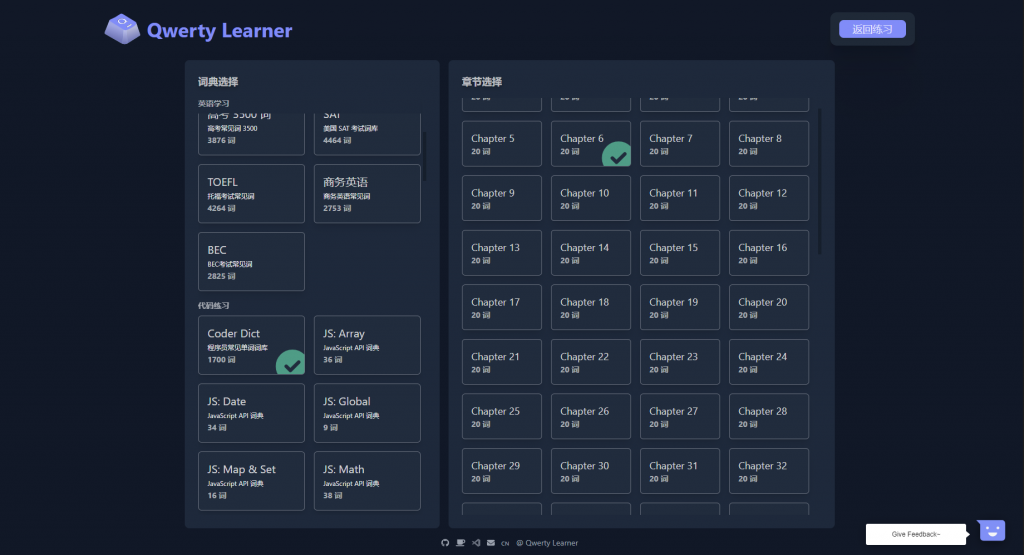
摸鱼网站+1,打字练习,词典可选JSAPI、英语四六级等
软件安装
Office Tool Plus
https://otp.landian.vip/zh-cn/download.html
激活office
https://www.coolhub.top/archives/14
Acrobat
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1uc8DKUGZTZjWQ54KL3TBKw
43kj
Github加速
将 raw.githubusercontent.com 替换为 raw.staticdn.net 即可加速
内循环遍历单位技巧
for(var a = 0; a < entitys.length; a++){
for(var b = a + 1; b < entitys.length; b++){
console.log(`${entitys[a].name}-${entitys[b].name}
distance:${entitys[a].GetDistance(entitys[b])}`);
}
}
内循环并没有遍历所有的单位。它只是遍历了外循环还没有访问过的单位。这样就避免了对 每一对单位进行两次比较,正着比一次,反着再比一次。如果我们已经处理过了A和B之间的 碰撞,我们就不再需要再次检测B和A之间的碰撞了。
UnityEngine.Animator HasState
int stateid = Animator.StringToHash(name);
if(animator.HasState(i, stateid)){
Debug.Log("存在状态:"+name);
}